Wells are a significant source of groundwater for agricultural, industrial, and domestic use since evolution. The efficiency and sustainability of these wells depend significantly on their specific yield and specific capacity. Understanding these concepts is essential to manage and utilize groundwater resources.
This blog post explains the definitions, significance, and factors affecting the specific yield and specific capacity of a well.
Specific Yield of Well
Definition: Specific yield, often expressed as a percentage, refers to the volume of water that a saturated soil or rock releases due to gravity.
It indicates the efficiency of an aquifer in releasing stored groundwater.
Significance of Specific Yield of a Well
- Water Availability: Higher specific yield means more water is available for extraction from the aquifer.
- Aquifer Management: This helps in estimating the groundwater reserves and planning sustainable extraction rates.
- Environmental Impact: It influences the recharge rates of aquifers and the sustainability of groundwater resources.
Calculation: Specific yield is calculated as the ratio of the volume of water that drains freely from the material due to gravity to the total volume of the material.
Mathematically, it can be expressed as:
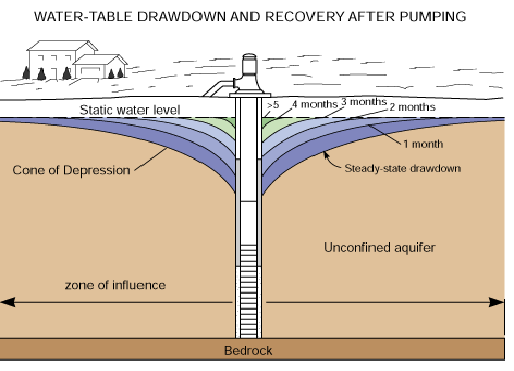
Specific Capacity of Well
Definition: Specific Capacity of a well is a measure of its efficiency, defined as the rate of water discharge per unit drawdown. It indicates how effectively a well can supply water, considering the drawdown caused by pumping.
Calculation: Specific capacity is calculated by dividing the pumping rate (Q) by the drawdown (s) observed in the well. Mathematically, it is expressed as:
where Q is the discharge rate (usually measured in liters per second or gallons per minute) and ss is the drawdown (measured in meters or feet).
Significance of Specific Capacity of Well
- Well Performance: Higher specific capacity indicates a more efficient well with a greater ability to deliver water.
- Maintenance and Design: This helps in diagnosing well performance issues and designing wells to optimize water delivery.
- Resource Management: This aids in managing and planning groundwater extraction to prevent over-pumping and depletion of the aquifer.
Factors Affecting Specific Yield and Specific Capacity of a well
- Aquifer Characteristics: The type of soil or rock, its porosity, permeability, and saturation level influence both specific yield and capacity.
- Well Design and Construction: Proper well design, casing, and screen placement enhance specific capacity.
- Pumping Rates: Excessive pumping can lead to higher drawdown, affecting the specific capacity negatively.
- Seasonal Variations: Changes in groundwater levels due to seasonal recharge or extraction patterns can impact specific yield and capacity.
- Aquifer Recharge: The rate at which an aquifer is replenished influences the sustainability of water extraction and the specific yield.
Read Also-
What is Aquifer, Aquiclude, Aquitard and Aquifuge?
IS 6512 1984 [Criteria for Design of Concrete Gravity Dams]