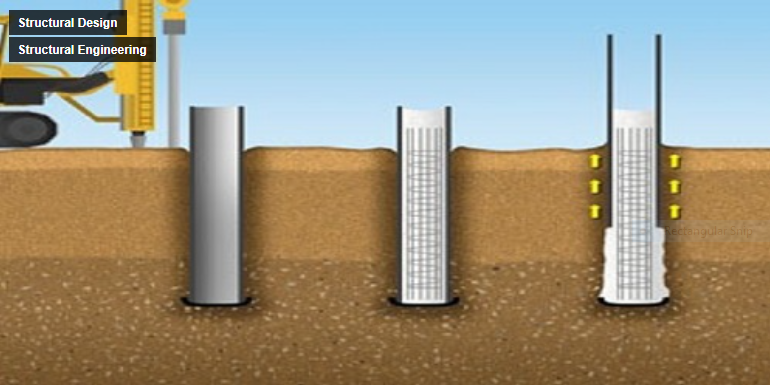
Pile foundations are a type of deep foundation. They are adopted when firm ground strata are not available at shallow depths or the load coming from the superstructure is excessive. The way pile foundation transfers the load to beneath soil is either by skin friction or by end bearing.
The construction cost of pile foundations as compared with shallow ones is also higher and skilled labor is also required. Also, technology to drive piles is a bit more costly than shallow foundations.
Pile foundations could be classified in many different ways.
- Classification Of Piles Based On Function
- Classification Of Piles Based On Material And Composition
Classification of Pile Foundation Based on Function
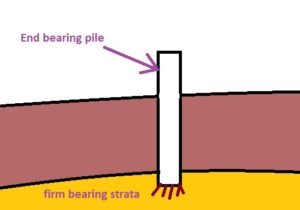
- End Bearing Pile Foundations: These types of piles transfer load coming from the superstructure, directly to the firm and hard ground. They are suitable when firm ground strata are available at comparatively shallow depths.
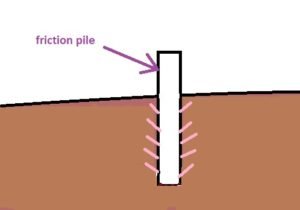
- Friction Piles: Friction piles are used in the case of footing in cohesive soil. If hard strata are available at greater depth, friction piles are chosen. Friction piles transfer load to the ground by friction between the skin of the pile and the ground.
- Compaction Piles: Compaction piles are so designed that they have very less strength. They do not carry any direct load, but they are used to compact loose granular sands. And thus, increasing the bearing capacity of the soil.
- Anchor Piles: These are well known for resisting uplift force and over-turning moment caused by hydrostatic pressure.
- Fender Piles and Dolphins: These are used to protect water front structures against the impact from ships or floating objects.
Classification of Pile Foundation Based on Material and Composition
- Concrete Piles:
- Precast Prestressed Piles: These types of piles are more economical than cast-in situ piles and also more economical.
- Cast in situ piles: The cast in situ concrete piles are created by first digging the hole in the ground and then placing the reinforcement and successively concreting is done.
- Timber Piles: These types of piles are either trunk of a tree or a trimmed branch. Timber piles being economic come with inherent other advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages of timber piles- Timber piles are easy to install on the site.
- As timber is a resilient material, a timber pile can be used when there are chances of shock loading.
- If there occurs any necessary to uninstall the timber pile as in case of temporary structure, timber piles are the best suited.
- In the case of part of a temporary structure timber pile offers all the necessities.
- Steel Piles: These types of piles found their uses in marine structures.
- Composite Piles: Composite piles are those which use piles of one material driven over the pile of another material.
- Concrete and timber
- Concrete and steel – The requirement of concrete steel pile arise when there is a limit to the depth of cast-in-situ concrete piles alone. In this type of system, first steel pile is driven into the ground and then the precast concrete pile is driven over it.
- Under Reamed Piles: Under Reamed Piles are bored cast in situ RCC piles. These types of foundations are ideally suited for black cotton soil. Under reamed piles have one, two, or more bulbs created beneath the ground by reaming tools. These bulbs are also known as reams. It is interesting to know that under ream pile foundations are developed by C.B.R.I. (Central Building Research Institute).
Negative Skin Friction Acting On Piles
It is caused by the settlement of loose soil surrounding the soil that adds a downward force to the pile. Negative skin friction is an unwanted phenomenon as it decreases the bearing capacity of the pile.
Read Also-
All You Want To Know About Caisson Foundation
What Is Liquefaction? (Process, Causes, And Mitigation)
Types of Foundations Used for Building Construction
Average Salary of Civil Engineer in USA
Foundation on Black Cotton Soil – Problems and Solutions