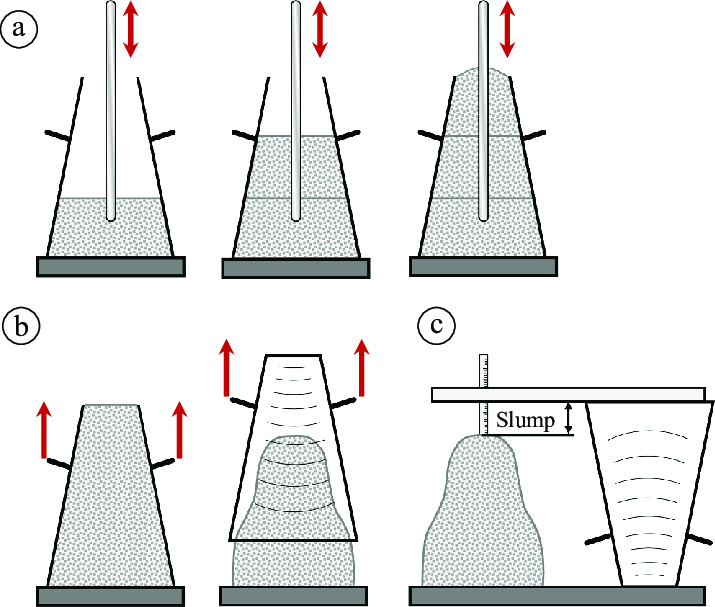
Workability of concrete means the ease with which it can be transported, placed, and compacted. Workability is an important property of concrete as it will be the final strength of hardened concrete. There are various methods to measure the workability of concrete.
- Slump Test
It is a field test and most popular in the USA. A frustum of cone having base of 20 cm, top width 10 cm and height of 30 cm is used. The slump value normally varies from 50 mm to 150 mm. - Compacting Factor Test
This is a lab test and more scientific way to measure workability of concrete. It is suited for medium to low workable concrete and is more accurate than the slump test.
The Compaction factor value ranges from 0.7 to 0.95. Higher the value of compaction factor higher is the workability. - Flow Table Test
This test measures the workability by percentage flow. The value varies from 0% to 150%. - Vee-Bee Consistometer Test
This test is suitable for very low workability concrete. - Kelly Ball Test
It is a field test that determines workability by depth of penetration of metal hemisphere weighing 13.6 kg.
Factors Affecting Workability of Concrete
- Water Cement Ratio – The higher the water cement ratio, the higher will be the workability. It is obvious as water will reduce the friction between aggregates.
- Use of Admixtures – Use of plasticizers and superplasticizers improves the workability of concrete. It also increases the setting time of concrete.
- Size of Aggregates – Use of bigger size of aggregates yields higher workability. As the specific surface of bigger aggregate is smaller, less cement gel is needed to lubricate.
- Shape of Aggregate – Irregular shape and rougher texture of angular aggregate shows less workability than the round shaped aggregate.
Concrete Slump Test International Standard
- American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM): ASTM Slump test standards are ASTM C 143, and ASTM C143M.
- The American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO): AASHTO Slump test standards are AASHTO T119, AASHTO BS1881.
- British & European standard: British & European Slump test standard is BS EN 12350-2.
- Indian Standard: IS 1199 – 1959
Read Also-
Types of Cement and Their Properties
Grades of Concrete and Mix Ratio