Camber is defined as “transverse slope provided on road for proper drainage of surface water”
Sometimes camber is also referred to as the cross slope of the road.
Benefits of Providing Camber
- Camber is a must for surface drainage. It is the main component that prevents water logging on the road.
- Camber increases the stability of the sub-base by providing proper drainage.
Read Also- Superelevation In Highway Design
Types of Camber Provided on Road
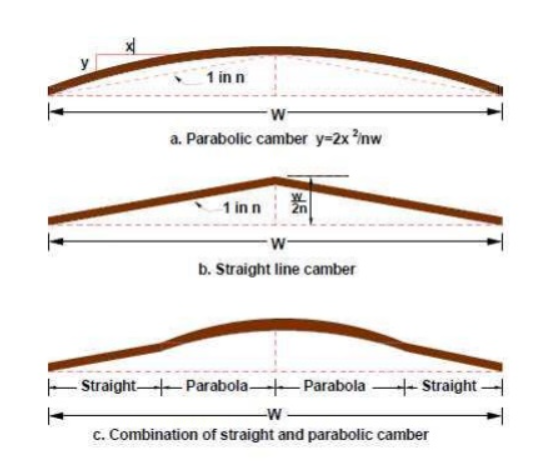
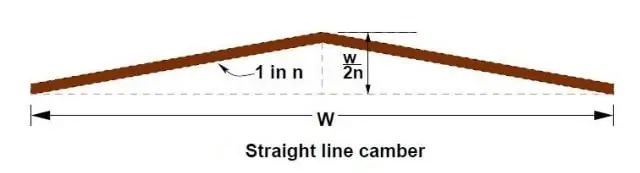
Sloped or Straight Camber
This type of camber consists of two straight slopes from edges meeting at the center of road cross-section. They are easy to construct and maintain.
Read Also- Classification Of Roads In India
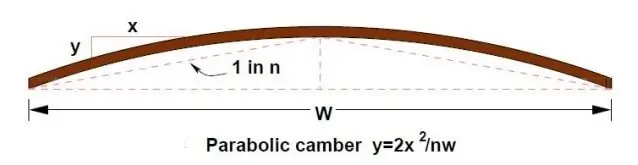
Parabolic Camber
This one is also known as barrel camber. It provides zero slope at the center of the road and maximum slope at the edges. This type of camber consists parabolic or elliptic curve.
Parabolic cambers are most suited for urban roads and fast-moving vehicles.
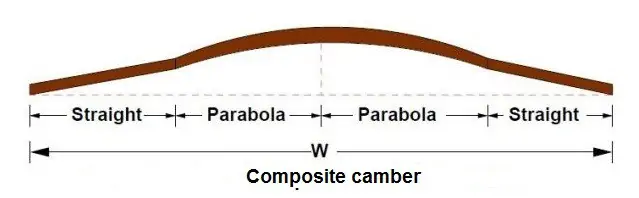
Composite camber
This is a combination of parabolic and straight camber. It includes two straight slopes from each of the edges of the road along with a parabolic camber at the center.
Recommended values of camber as per IRC standard
| Sr No. | Type of Road Surface | Heavy Rain Fall | Low Rain Fall |
| 1. | Cement Concrete and thick bituminous surface | 1 in 50 or 2.0% | 1 in 60 or 1.0% |
| 2. | Thin Bituminous surface | 1 in 40 or 2.5% | 1 in 50 or 2.0% |
| 3. | Water Bound Macadam and gravel pavement | 1 in 33 or 3.0% | 1 in 40 or 2.5% |
| 4. | Earth Road | 1 in 25 or 4.0% | 1 in 33 or 3.0% |
Read Also- Grades Of Concrete And Mix Ratio
Hydraulic Cement – Properties and Applications
Types of Cement, Their Properties and Applications
External Resources- ASCE Journal Of Transportation Engineering
Camber is transverse slope provided on surface for proper drainage of pavement.